Introduction
htop is an interactive system-monitor process-viewer and process-manager. It is designed as an alternative to the Unix program top. It shows a frequently updated list of the processes running on a computer, normally ordered by the amount of CPU usage.
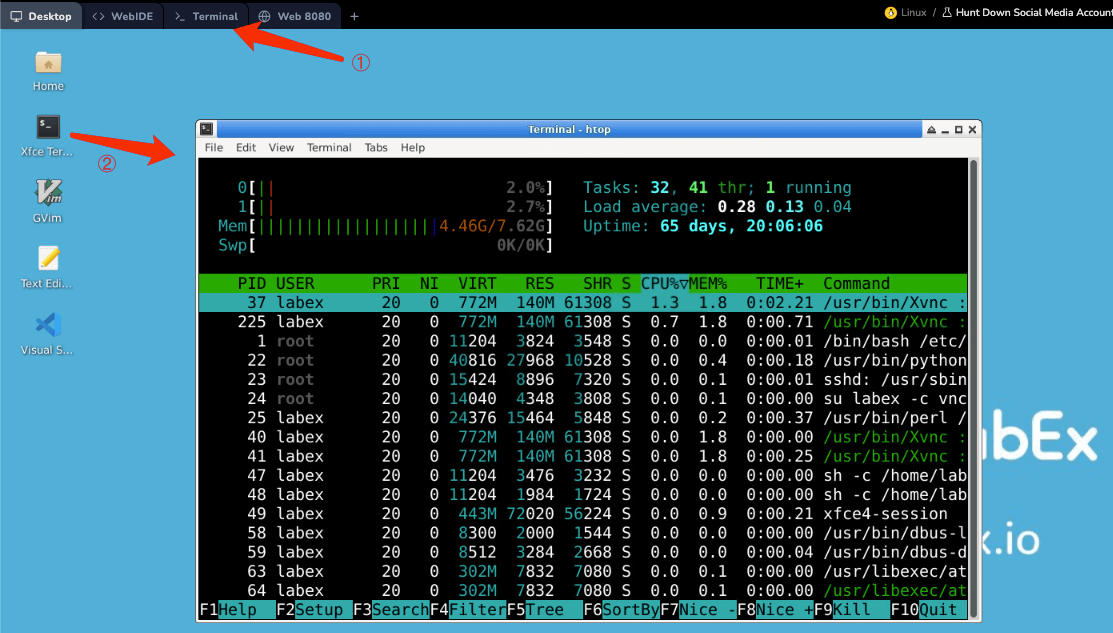
Unlike top, htop provides a full list of processes running, instead of the top resource-consuming processes. htop uses color and gives visual information about processor, swap and memory status.



