Creación de una Función Reutilizable para Superposiciones de Imágenes
Para hacer nuestro código más reutilizable, vamos a crear una función que pueda agregar una superposición de imagen a cualquier figura de Matplotlib. De esta manera, podemos aplicar fácilmente el mismo efecto a diferentes gráficos.
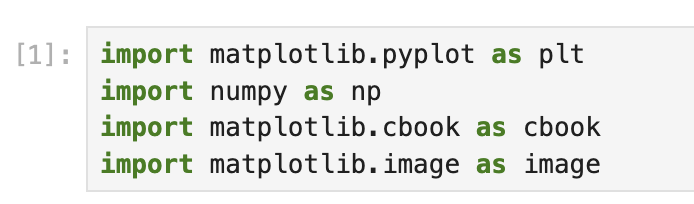
- Crea una nueva celda en tu cuaderno (notebook) e introduce el siguiente código:
def add_image_overlay(fig, image_path, x_pos=25, y_pos=25, alpha=0.5, zorder=3):
"""
Add an image overlay to a matplotlib figure.
Parameters:
-----------
fig : matplotlib.figure.Figure
The figure to add the image to
image_path : str
Path to the image file
x_pos : int
X position in pixels from the bottom left
y_pos : int
Y position in pixels from the bottom left
alpha : float
Transparency level (0 to 1)
zorder : int
Drawing order (higher numbers are drawn on top)
Returns:
--------
fig : matplotlib.figure.Figure
The figure with the image overlay
"""
## Load the image
with cbook.get_sample_data(image_path) as file:
im = image.imread(file)
## Add the image to the figure
fig.figimage(im, x_pos, y_pos, zorder=zorder, alpha=alpha)
return fig
## Example usage: Create a scatter plot with an image overlay
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
## Set a random seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
## Generate random data for a scatter plot
x = np.random.rand(50) * 10
y = np.random.rand(50) * 10
## Create a scatter plot
ax.scatter(x, y, s=100, c=np.random.rand(50), cmap='viridis', alpha=0.7)
ax.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis Label')
ax.set_title('Scatter Plot with Image Overlay')
## Add the image overlay using our function
add_image_overlay(fig, 'logo2.png', x_pos=50, y_pos=50, alpha=0.4)
## Display the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
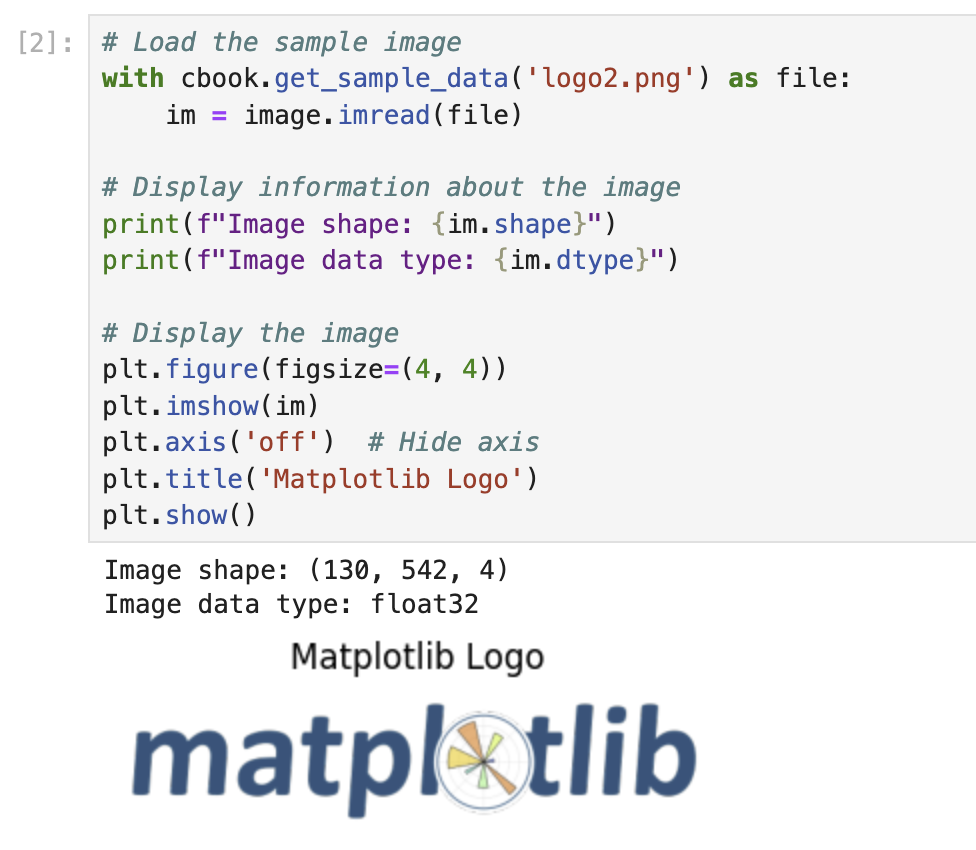
Este código define una función llamada add_image_overlay que:
- Toma parámetros para la figura, la ruta de la imagen, la posición, la transparencia y el orden de dibujo (z-order).
- Carga la imagen especificada.
- Agrega la imagen a la figura utilizando
figimage.
- Devuelve la figura modificada.
Después de definir la función, demostramos su uso creando un gráfico de dispersión con datos aleatorios y agregando el logotipo de Matplotlib como superposición.
- Ejecuta la celda presionando Shift+Enter.
La salida debe mostrar un gráfico de dispersión con puntos de posición y color aleatorios, y el logotipo de Matplotlib superpuesto en la posición (50, 50) con una opacidad del 40%.
- Vamos a probar otro ejemplo con un gráfico de línea. Crea una nueva celda e introduce el siguiente código:
## Example usage: Create a line plot with an image overlay
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
## Generate data for a line plot
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
## Create a line plot
ax.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='#d62728')
ax.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis Label')
ax.set_title('Sine Wave with Image Overlay')
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
## Add the image overlay using our function
## Place it in the bottom right corner
fig_width, fig_height = fig.get_size_inches() * fig.dpi
with cbook.get_sample_data('logo2.png') as file:
im = image.imread(file)
x_pos = fig_width - im.shape[1] - 50 ## 50 pixels from the right edge
add_image_overlay(fig, 'logo2.png', x_pos=x_pos, y_pos=50, alpha=0.6)
## Display the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Este código crea un gráfico de línea que muestra una onda sinusoidal y agrega el logotipo de Matplotlib en la esquina inferior derecha del gráfico.
- Ejecuta la celda presionando Shift+Enter.
La salida debe mostrar un gráfico de línea de una onda sinusoidal con el logotipo de Matplotlib superpuesto en la esquina inferior derecha con una opacidad del 60%.
Estos ejemplos demuestran cómo nuestra función add_image_overlay se puede utilizar para agregar fácilmente superposiciones de imágenes a diferentes tipos de gráficos, lo que la convierte en una herramienta versátil para personalizar visualizaciones.